DO I NEED MY OWN SYSTEM? Maybe!
DOES CULLIGAN HAVE A DEIONIZATION EXCHANGE PROGRAM? Absolutely!
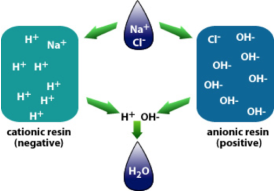
Deionization systems can be expensive to buy, install, and most importantly maintain but Culligan delivers the expertise and integration you need.
- Culligan also provides Deionization Exchange Service that eliminates capital investment while providing all the benefits of your own DI process without regulatory training and constraints.
- DI Exchange tanks will be plumbed directly into your water supply and can be exchanged as needed.
- Regardless of the flow needed, once the resin tanks are exhausted, they’re simply exchanged on a regular schedule and regenerated off-site.
No matter which option is right for you and your business, Culligan will help you determine your requirements and provide an affordable solution.